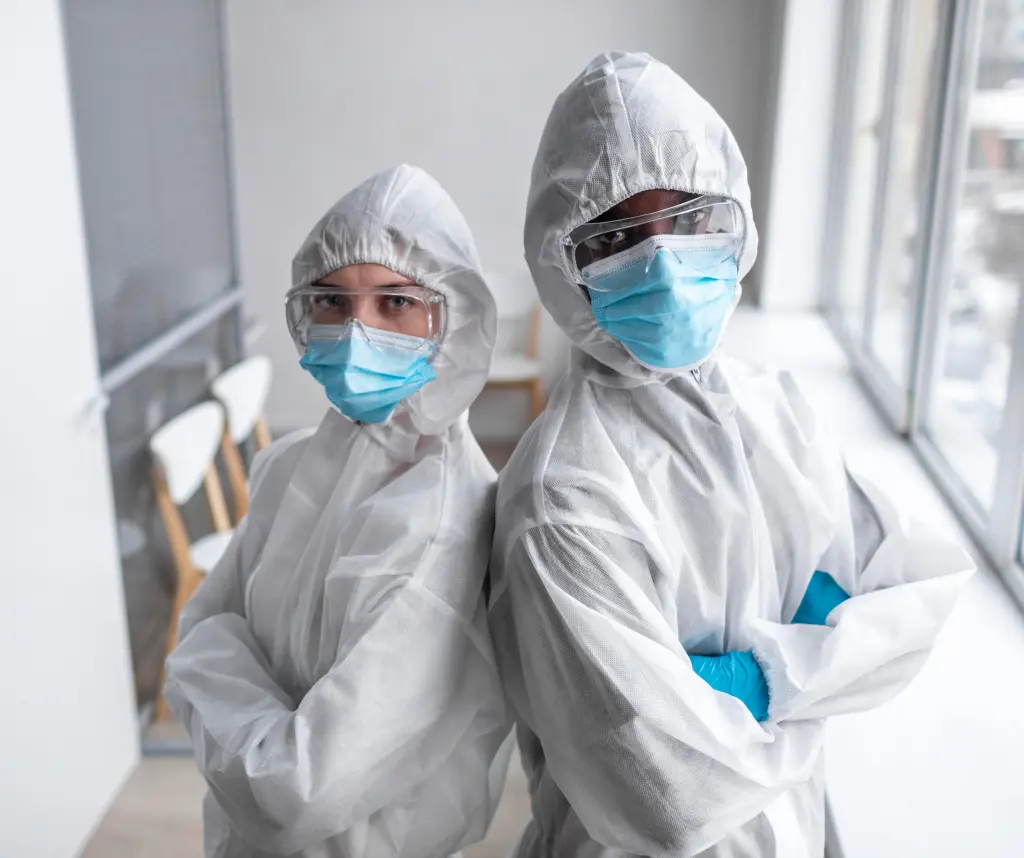
China is currently experiencing a rapid spread of the human metapneumovirus (HMPV), raising global health concerns five years after the COVID-19 pandemic. HMPV, a respiratory virus, is known to cause symptoms ranging from mild cold-like issues to severe respiratory distress, particularly in children, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals.
What is HMPV?
HMPV belongs to the Pneumoviridae family and was first identified in 2001. It primarily targets the respiratory system and is transmitted through respiratory droplets. Symptoms include fever, cough, nasal congestion, and in severe cases, pneumonia.
Symptoms of HMPV
Mild Symptoms:
- Fever
- Cough
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Sore throat
Severe Symptoms (in high-risk groups):
- Wheezing
- Shortness of breath
- Difficulty breathing
- Rash or skin irritation
At-Risk Groups:
- Young children
- Older adults
- People with weakened immune systems or chronic health conditions
How Does HMPV Spread?
HMPV spreads through respiratory droplets and contaminated surfaces. Common transmission methods include:
- Direct contact: Touching or being close to an infected person who is coughing or sneezing.
- Contaminated surfaces: Virus particles on objects like phones, door handles, or keyboards can be transmitted when touched.
- Close interactions: Physical contact such as hugging, shaking hands, or kissing.
Preventing HMPV Infections
Although there is currently no vaccine for HMPV, several preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of infection:
- Hand Hygiene: Regularly wash hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
- Avoid Touching Face: Avoid touching your nose, mouth, or eyes with unwashed hands.
- Mask Up: Wear masks in crowded or high-risk areas to prevent inhaling respiratory droplets.
- Disinfect Surfaces: Regularly clean commonly touched surfaces like doorknobs, countertops, and electronic devices.
- Stay Home if Sick: Avoid going to work or public places if you are feeling unwell to prevent spreading the virus.
How is HMPV Treated?
Currently, there is no specific antiviral medication to treat HMPV. Treatment is focused on alleviating symptoms and providing supportive care:
Medical Interventions: Severe cases may require oxygen therapy or hospitalization for respiratory support.
Why is HMPV Gaining Attention?
Rest and Hydration: Ensure proper hydration and take adequate rest to support recovery.
Over-the-Counter Medications: Use medications to reduce fever and relieve symptoms, as advised by a healthcare provider.
HMPV outbreaks have been sporadic globally, but the current surge in China indicates the potential for widespread transmission. Experts attribute this to:
- Increased human interaction post-pandemic.
- Immunological gaps left by reduced exposure to viruses during COVID-19 lockdowns.
Is HMPV Comparable to COVID-19?
Unlike COVID-19, HMPV is not as contagious or severe. However, its impact on vulnerable groups can be significant, necessitating early diagnosis and intervention.
Prevention and Treatment
- Prevention Measures:
- Regular handwashing and use of masks.
- Avoiding crowded spaces during outbreaks.
- Treatment Options:
- Supportive care such as hydration and oxygen therapy.
- No specific antiviral treatment is currently available, but clinical trials are ongoing.
The Global Response
Countries are closely monitoring the situation in China. Increased surveillance and research into vaccines and treatments are being prioritized to prevent another global health crisis.
FAQs
1. What is human metapneumovirus (HMPV)?
HMPV is a respiratory virus that causes symptoms ranging from mild colds to severe respiratory illness, particularly in vulnerable populations.
2. How is HMPV transmitted?
It spreads through respiratory droplets, direct contact with infected individuals, or contaminated surfaces.
3. Who is most at risk of severe HMPV infection?
Children, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals are at higher risk of severe symptoms.
4. Is there a vaccine for HMPV?
Currently, no vaccine exists for HMPV, but research is ongoing.
5. How can HMPV infections be prevented?
Preventive measures include regular handwashing, mask-wearing, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals.